The Short Answer: Fixing a concrete slab foundation involves several repair methods depending on the foundation issue. Small cracks can be sealed with epoxy injections, while larger cracks may require carbon fiber reinforcement. For sinking foundation problems caused by soil conditions or differential settlement, push piers or helical piers are installed to stabilize and lift the slab. Slab leaks from leaking pipes require accessing water lines beneath the concrete slab.
Slab foundations are popular for their cost-effectiveness and simplicity, but they can present unique challenges for homeowners. In this article, we’ll explore the most effective solutions for fixing slab foundation problems, how to identify when your concrete slab foundation needs repair, and provide practical guidance on choosing the right repair methods.
What Is A Slab Foundation & What Problems Do They Face?
A concrete slab foundation serves as both the floor and structural support for your home. Unlike traditional foundations that incorporate crawl spaces or basements, slab homes are built directly on a solid concrete base that rests on the ground. In this design, plumbing and electrical lines are often embedded within or beneath the slab. This construction method is popular in many regions due to its lower cost, faster build time, and minimal maintenance needs, especially in warmer climates where ground freezing is less of a concern.
The Top Problems With Slab Foundations
1. Not Suitable For Freezing Climates
One significant drawback of slab homes is their unsuitability for freezing climates. Slab foundations are typically built above the frost line, increasing their chance of being affected by frost heave. Frost heave happens when soil expands from freezing water, creating pressure that lifts or cracks the slab. While frost-protected slab foundations exist, they are still more likely to face damage from frost than other foundation types.
2. Slab Cracks
Slab homes are more likely to experience severe foundation cracks than other foundation types. Damage may come from shifting soil, tree roots, freezing temperatures, or natural disasters. These cracks compromise the home’s structural integrity and can lead to other issues, such as water infiltration and mold growth. All foundations are subject to cracking, but a slab foundation often displays the associated symptoms more readily and will require quick repairs to avoid escalating the problems.
3. Difficult To Access Utilities
In slab homes, utilities like plumbing and electrical wiring are often embedded within the concrete slab. Accessing these utilities requires cutting through the concrete, which can be labor-intensive and costly.
4. Lack Of Storage
The absence of a basement or crawl space means limited storage options for HVAC systems and personal belongings. Hence, part of the home’s floor space must be dedicated to housing the HVAC system, and there are fewer places for storing seasonal items unless you invest in a shed or attic.
5. Aesthetic Issues
Some homeowners find slab homes less attractive compared to homes with raised foundations. The lack of elevation can make the exterior appear flat and unappealing. Additionally, landscaping options may be limited due to the slab’s proximity to the ground.
Warning Signs That Your Slab Foundation Needs Repair
Recognizing the signs that indicate potential foundation problems with your concrete slab foundation helps you address issues before they become expensive repairs.
Key Indicators Your Slab Foundation Needs Attention
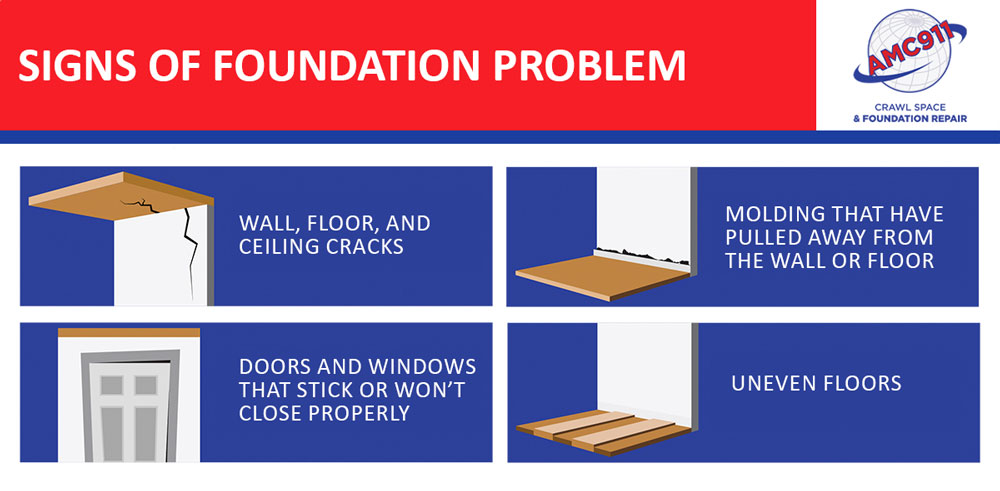
Visible Cracks: Large or expanding cracks in the slab, floors, walls, or ceiling indicate significant slab foundation problems. If you can fit a coin into the crack, it requires immediate inspection by a foundation repair expert.
Uneven Floors: Floors that are no longer level or appear to be sinking signal foundation problems. You might notice marbles rolling across the room or gaps between the floor and baseboards.
Sticking Doors and Windows: Difficulty opening or closing doors and windows often stems from foundation shifts. As your concrete slab foundation moves, it causes the frame of your home to become misaligned.
Separation of Molding: Gaps forming between molding and walls or floors indicate foundation movement.
Signs of Water Damage: Moisture issues, evidence of a foundation leak, or unexplained water pooling may indicate slab leak problems. Musty odors, mold growth, or unusually high water bills can also signal leaking pipes beneath your slab.
If you notice any of these warning signs, contact a foundation repair company for an inspection.
Professional Foundation Repair Methods For Fixing Slab Foundations
Repairing a damaged slab foundation requires expert intervention. Here are the standard foundation repair methods used by professionals:
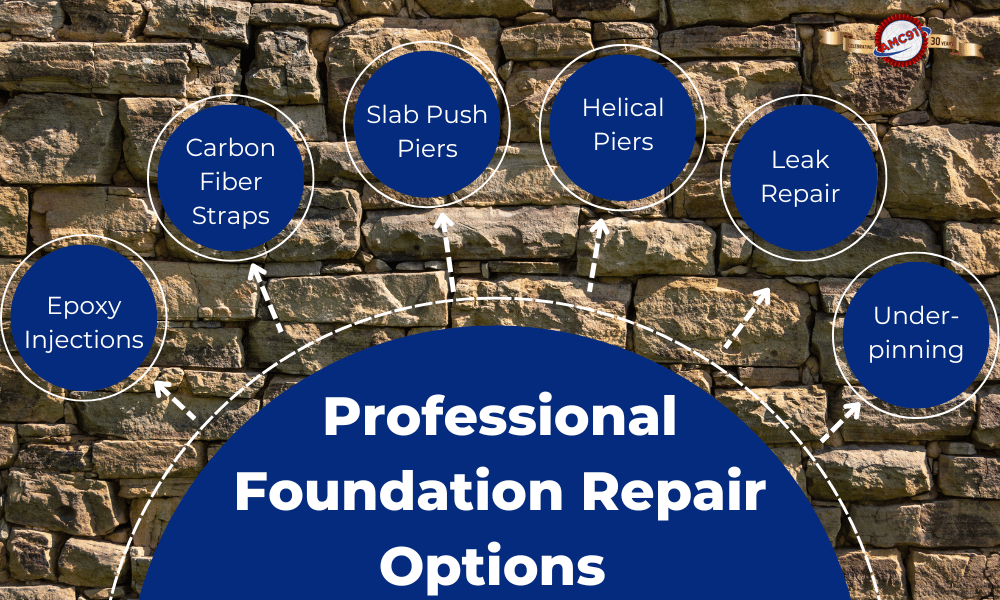
Epoxy Injections
Epoxy injections work well for small cracks in your concrete slab. This foundation repair method provides a moisture-proof seal while reinforcing structural integrity. The epoxy penetrates deep into cracks, bonding broken segments together and preventing further damage. This cost-effective solution addresses early-stage foundation cracks before they expand.
Carbon Fiber Straps
Carbon fiber reinforcement is ideal for larger cracks that threaten your foundation’s stability. These straps are strong, lightweight, and minimally invasive. Foundation repair experts bond them to your concrete foundation using epoxy resin. This effective solution prevents further crack movement and adds long-term stability without compromising interior space.
Slab Push Piers
Push piers are a standard solution for stabilizing and lifting settled slab foundations. This steel pier system is hydraulically driven into the ground using a hydraulic jack until reaching stable soil that can support your home’s weight.
The process involves:
- Exposing small sections of your slab
- Installing push piers underneath the foundation
- Driving piers to load-bearing soil depth
- Transferring your building’s weight onto the pier system
Push piers provide long-lasting support and prevent further foundation settlement. They’re an effective solution for sinking foundation issues caused by soil conditions that can’t support the structure’s weight.
Helical Piers
Helical piers offer an alternative to push piers for certain soil conditions. Their screw-like design makes them ideal for expansive clay soil or sandy soil. A structural engineer can determine which pier system provides the best solution for your specific situation.
Polyurethane Foam Injection
Polyurethane foam injection lifts sunken concrete slabs by filling voids beneath the slab created by soil erosion. This lightweight but strong material expands to raise your foundation back to its proper level. This effective solution is less invasive than pier installation and offers a quick repair process with minimal disruption to your home.
Underpinning
Underpinning levels uneven floors caused by differential settlement. This approach reinforces your foundation by extending it to load-bearing soil strata using either push piers or helical piers. Foundation repair experts use underpinning in areas with weak or shifting soil where surface-level repairs won’t provide adequate support.
Slab Leak Repair
Slab leaks require accessing water lines beneath your concrete slab. The repair process may involve cutting through the concrete to reach the leaking pipe, repairing or replacing the damaged section, and addressing any water intrusion damage. In some cases, re-routing water lines around the problem area proves more cost-effective.
Understanding Foundation Repair Costs And Finding Expert Help
What Affects Foundation Repair Cost
Several factors influence the total cost of fixing your slab foundation:
- Severity of foundation problems
- Type of repair method needed
- Extent of structural damage
- Accessibility and soil conditions
- Size of the affected area
Foundation repair costs vary significantly by project. Early intervention typically reduces your foundation repair cost because problems are easier to fix before they escalate.
Why Professional Foundation Repair Matters
Foundation issues require specialized expertise. Foundation repair companies provide a proper assessment, accurate diagnosis, and engineered solutions that address the root cause. A structural engineer’s evaluation confirms what’s causing your foundation problems. Professional crews have specialized equipment like hydraulic jack systems and pier installation tools that aren’t available to homeowners.
What To Look For In Foundation Repair Companies
When choosing a foundation repair expert, consider these factors:
- Experience specifically with slab foundation repair
- In-house engineering team
- Proper licensing and insurance
- Professional, uniformed crews
- Comprehensive services including foundation, crawl space, and waterproofing
- Warranty coverage on repairs
Don’t wait if you’re experiencing foundation issues with your concrete slab foundation. The common problem of delaying repairs only leads to more expensive solutions down the road.
Protect Your Home With Professional Foundation Repair
AMC911 Crawl Space & Foundation Repair has been providing engineered foundation repair solutions for over 30 years. Serving homeowners throughout Hampton Roads and the Eastern Shore of Virginia, our family-owned company holds Class A contractor licensing and maintains an A+ rating with the Better Business Bureau.
Our in-house engineering team designs custom solutions for each unique foundation problem, and our professional crews handle installation using proven repair methods. From addressing slab foundation problems and crawl space issues to comprehensive waterproofing services, we offer complete protection for your home’s foundation.
If you’re dealing with slab leaks, uneven floors, foundation cracks, or any other slab foundation repair needs, schedule an inspection to get an expert evaluation and repair quote.